
Having worked as a neurosurgeon for many years, I’ve seen firsthand the impact that brain tumors can have on patients and their families. It’s a complex and often daunting diagnosis, but understanding the basics can help demystify it. Let me share some key information about brain tumors, their types, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Exactly Is a Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within the brain or the central spinal canal. There are two main types: benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors tend to grow slowly and don’t spread to other parts of the body, but they can still cause significant problems by pressing on brain tissues. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, can grow rapidly and invade nearby tissues.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Brain Tumors
Symptoms of brain tumors vary depending on the tumor’s size, type, and location in the brain. Common symptoms include headaches, often worse in the morning, seizures, nausea and vomiting, and changes in personality or behavior. Some people might experience problems with balance, hearing, or vision. Because these symptoms can be caused by many different conditions, it’s essential to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
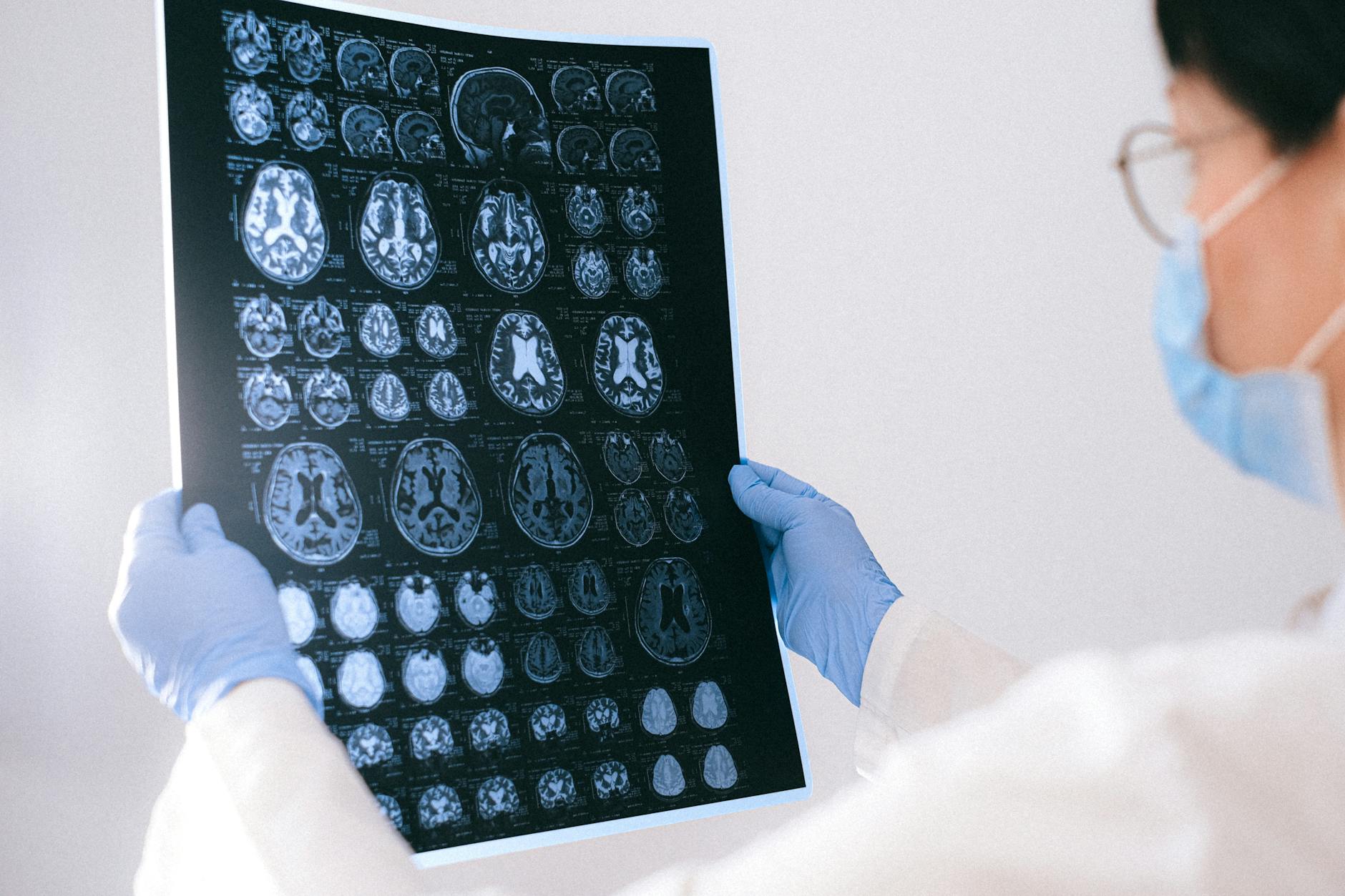
Diagnosing a brain tumor typically involves a combination of neurological exams and imaging tests. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the most commonly used tool, as it provides detailed images of the brain. Sometimes, a computed tomography (CT) scan is used. In certain cases, a biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of the tumor tissue for examination, is necessary to determine the exact type of tumor.

Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
Treatment for brain tumors depends on several factors, including the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Surgery is often the first step in treating a brain tumor. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without damaging surrounding brain tissue. For some tumors, complete removal might not be feasible, and other treatments like radiation therapy or chemotherapy are used to target the remaining tumor cells.
Advances in Surgical Techniques
Advancements in neurosurgical techniques have significantly improved outcomes for patients with brain tumors. Techniques like stereotactic surgery, which uses 3D imaging to precisely target the tumor, and awake craniotomy, where the patient is awake during part of the surgery to help protect critical brain functions, have made surgeries safer and more effective.
The Role of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill tumor cells. It can be used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells or as the primary treatment if surgery isn’t an option. Techniques like stereotactic radiosurgery, which delivers a high dose of radiation to a precise area, minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. These drugs can be taken orally or administered intravenously. While chemotherapy is often associated with systemic side effects, newer targeted therapies are designed to specifically attack cancer cells with fewer side effects. The American Cancer Society provides extensive information on chemotherapy and targeted therapy options.
Supportive Care and Rehabilitation
Living with a brain tumor can be challenging, but supportive care and rehabilitation can significantly improve quality of life. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can help patients regain lost functions. Support groups and counseling can also provide emotional support for both patients and their families.
Importance of Regular Follow-Ups
Regular follow-ups are crucial for monitoring the patient’s progress and detecting any recurrence early. This often involves periodic MRI or CT scans and neurological exams. It’s important to stay in close communication with your healthcare team and report any new symptoms immediately.
Research and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research and clinical trials are essential for developing new treatments and improving outcomes for brain tumor patients. Participating in a clinical trial can provide access to cutting-edge therapies that are not yet widely available. The National Cancer Institute offers a searchable database of clinical trials for brain tumor patients.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Proactive
Understanding brain tumors is the first step in taking control of your health. Staying informed about the latest treatments and maintaining open communication with your healthcare team can make a significant difference. If you or a loved one is dealing with a brain tumor, don’t hesitate to seek out the best possible care and support. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and advances in medical science are continuously improving the outlook for brain tumor patients.
